1. What is decay in enamel treatment ?
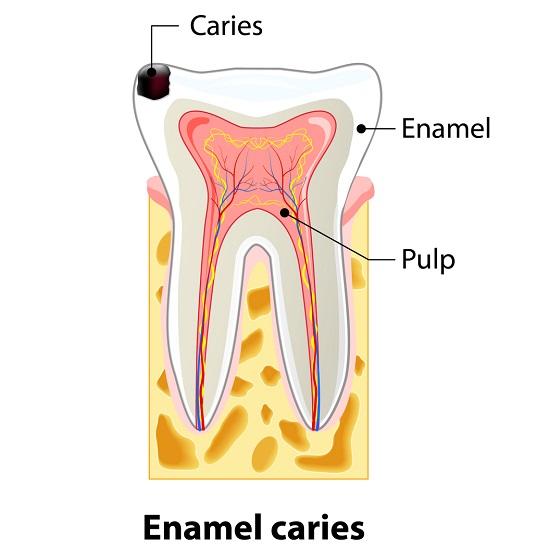
Enamel is the hard, outermost protective covering of the tooth. Enamel decay exposes the dentin layer and possibly the nerves within the tooth Enamel gets a lot of wear throughout the day. This hard tooth surface may already be strong, but caring for it prevents enamel decay and is crucial to your overall health. Everything you sip or chew passes across the surface of your teeth and can cause enamel erosion. And because enamel is calcified - meaning it contains no living cells - it can't regenerate once you lose it.
Enamel decay exposes the yellowish hard tissue called dentin, causing your teeth to look dingy or yellow as a result. This dentin contains microscopic canals that can carry substances straight to the pulp at the center of the tooth where all the nerves live, which is why your teeth might feel sensitive when you take a bite of ice cream or a sip of hot coffee.
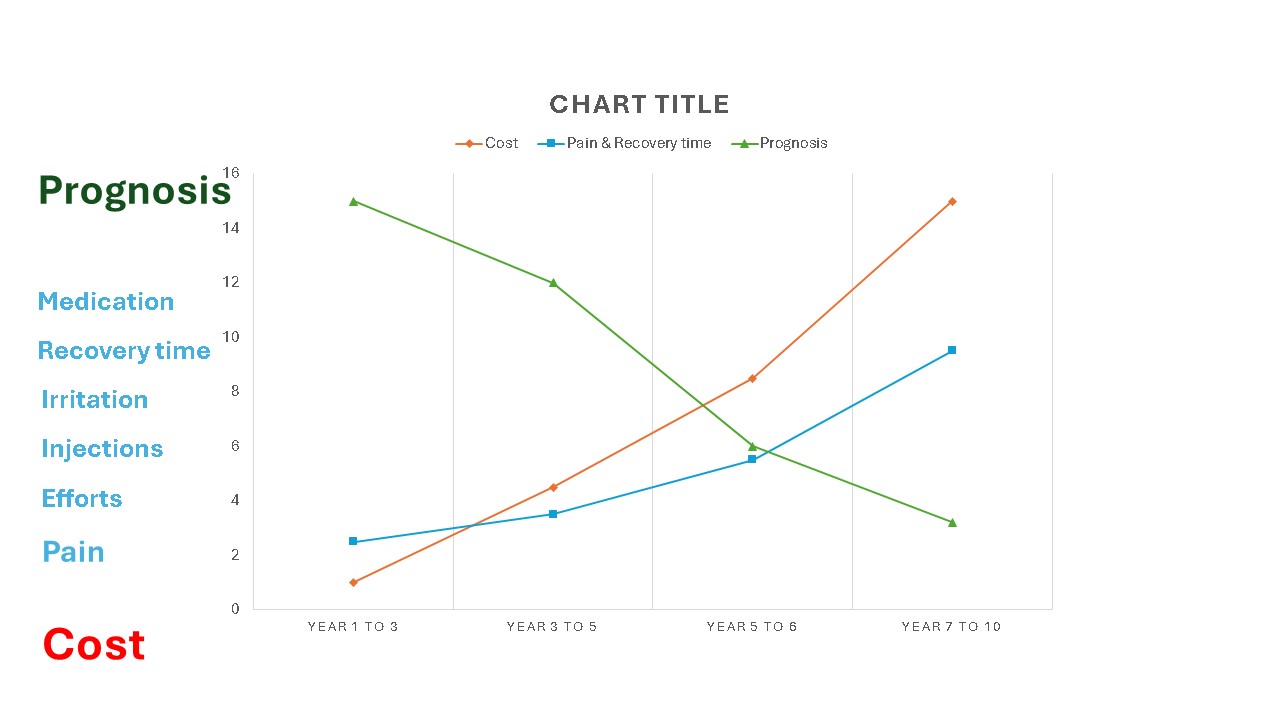
You may jog before work and turn in early to get your beauty sleep, but the heart and brain aren't the only things that need to run on all cylinders. Don't forget the health of your mouth! The first signals of enamel decay are sensitivity and changes to the color of your teeth. With this type of intel, you can give your pearly whites the attention they deserve.
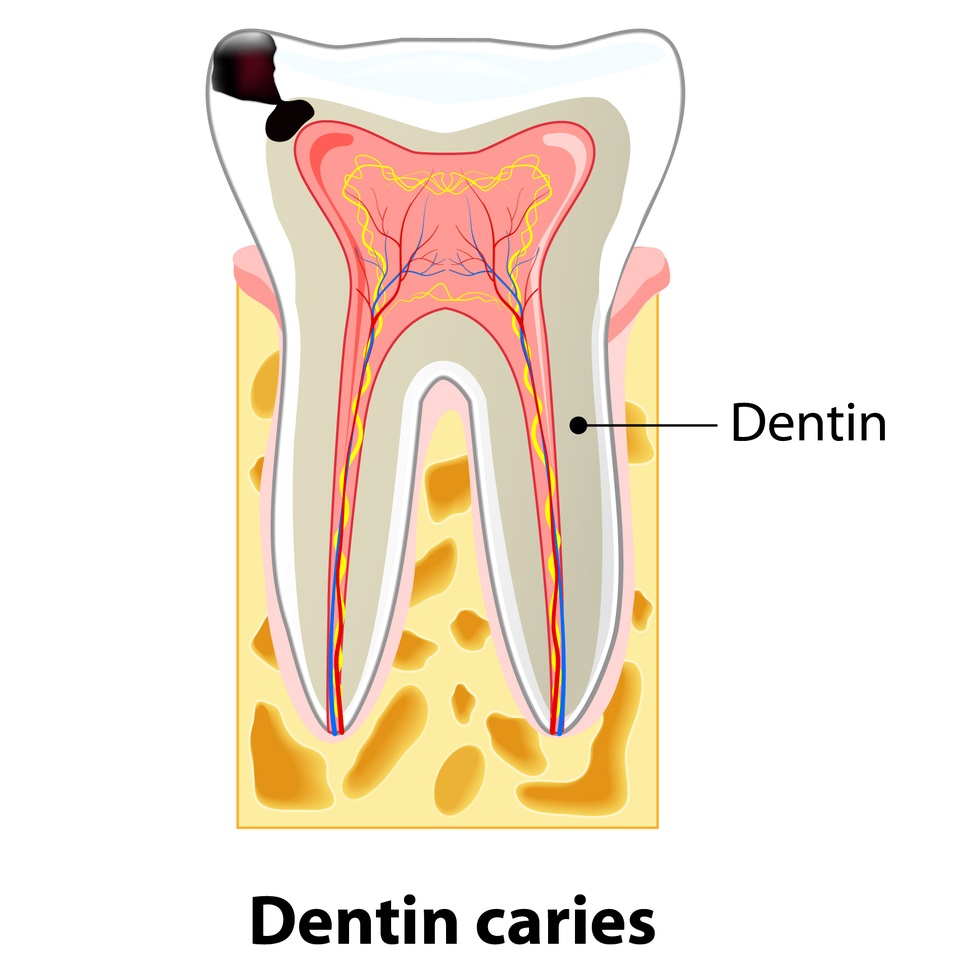
2. What is decay in dentin treatment ?
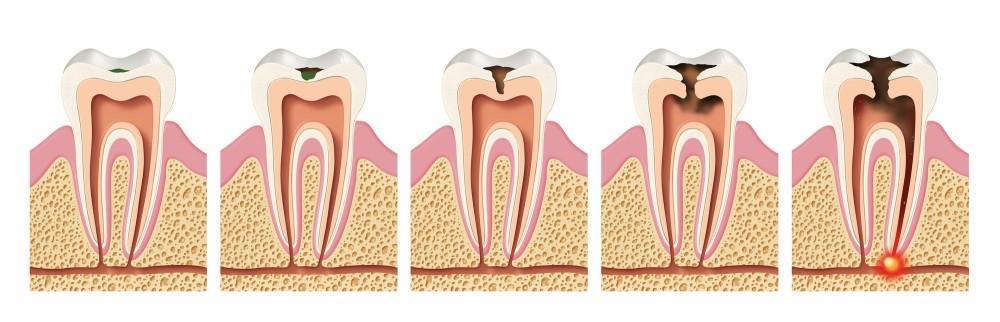
Decay now progresses beyond the enamel and starts to infect the dentin. This layer of your tooth, though still made of minerals, is far more porous. This means decay progresses more quickly. The hole in the tooth gets bigger, faster. Levels of discomfort and sensitivity will intensify. The dentist can still use a filling to repair the damage, or larger cavities may require inlays or onlays, a more extensive restoration.
In this stage, the decay progresses beyond the enamel into the dentin. At this juncture, your dentist can still restore the affected tooth with a filling. The pain levels also start intensifying along with the many stages of tooth decay. Any dental pain should be immediately noted so that the problem can be dealt with soon.
You may jog before work and turn in early to get your beauty sleep, but the heart and brain aren't the only things that need to run on all cylinders. Don't forget the health of your mouth! The first signals of enamel decay are sensitivity and changes to the color of your teeth. With this type of intel, you can give your pearly whites the attention they deserve.
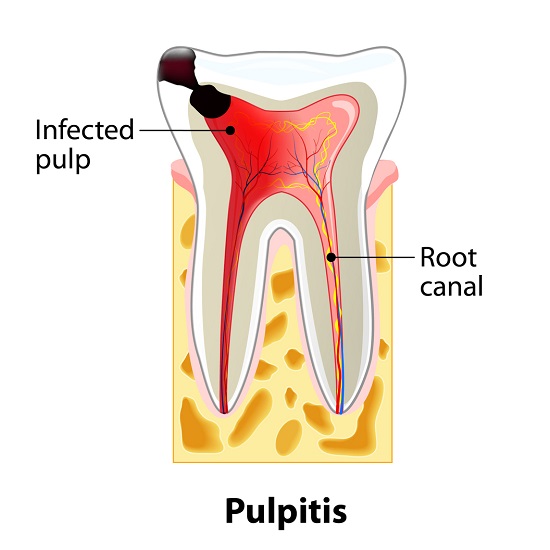
3. What is decay in pulp treatment ?
The dental pulp is the part in the center of a tooth made up of living connective tissue and cells called odontoblasts. The dental pulp is a part of the dentin pulp complex (endodontium).
If a tooth has been broken or damaged by decay, your dentist will try to fix it with a filling, crown or other dental treatment. But when there's too much damage for the tooth to be repaired, the tooth may need to be extracted or removed from its socket in the bone.
Beyond damage and decay, here are some other common reasons for tooth removal:
Some people have extra teeth that block other teeth from coming in.
Sometimes baby teeth don't fall out in time to allow the permanent teeth to come in.
People getting braces may need teeth extracted to create room for the teeth that are being moved into place.
People receiving radiation to the head and neck may need to have teeth in the field of radiation extracted.
People receiving cancer drugs may develop infected teeth because these drugs weaken the immune system. Infected teeth may need to be extracted.
Wisdom teeth, also called third molars, are often extracted either before or after they erupt in the mouth. They commonly come in during the late teens or early 20's. They need to be removed if they are decayed, infected, or if there is not enough room in the mouth.
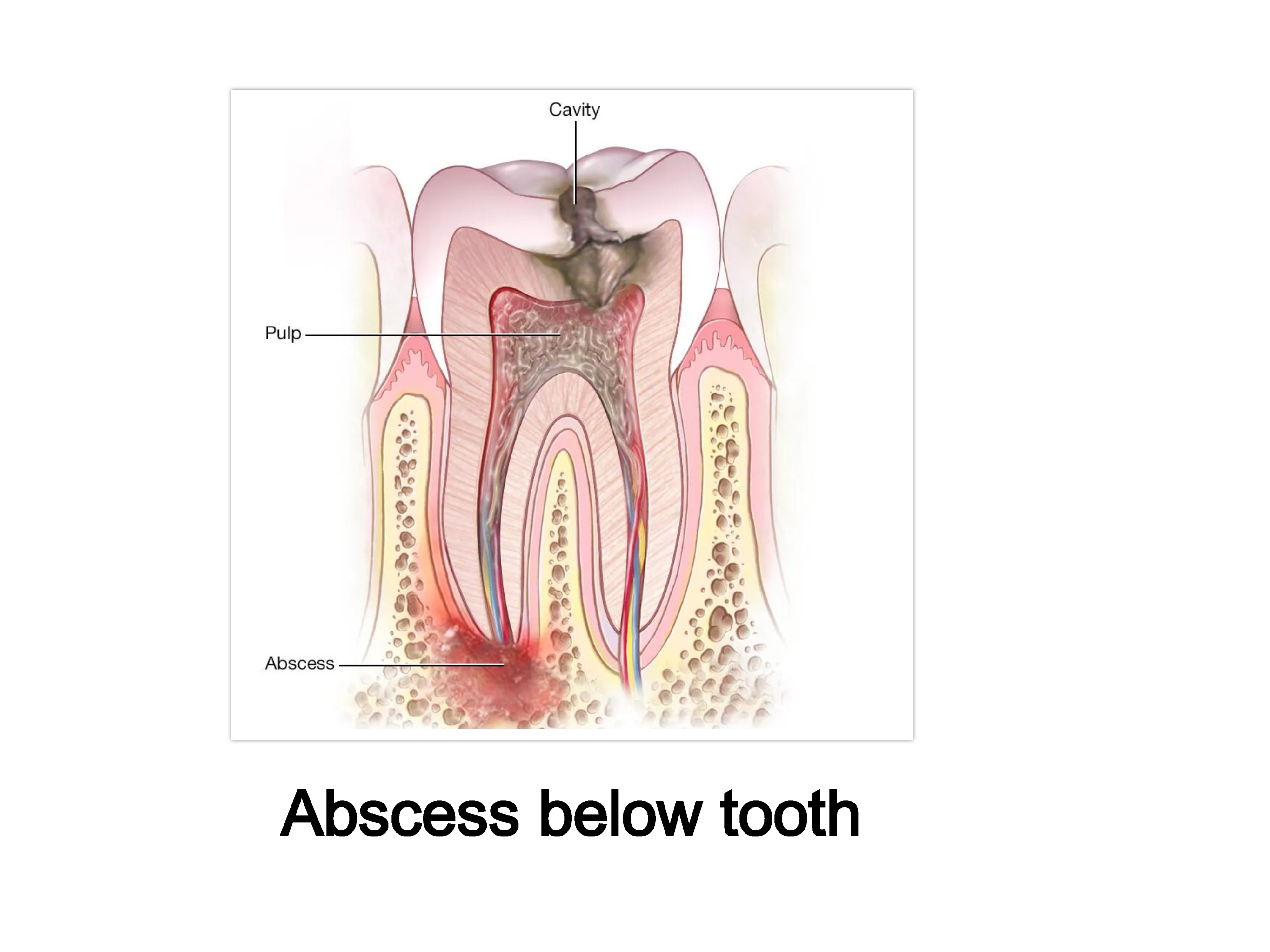
4. What is dental abscess treatment ?
An abscess is an infection in or around the root of the tooth which may or may not be painful. It occurs when the pulp, the soft tissue inside the root canal, dies and becomes inflamed and goes untreated.
The most common symptom of an abscess is an ache in the bone around the tooth, but you may also experience pain when chewing, swelling of the gums, or other symptoms. If you have ongoing pain or suspect an abscess, see an endodontist, who specializes in treating infected teeth and pulp.
A dental abscess is usually treated with root canal treatment or endodontic surgery. An endodontist will remove the bacteria from the empty canals within your tooth, clean, shape and fill the root canals, and seal the space.
You will return to your dentist, who will place a crown or other restoration on the tooth to protect and restore it to full function. After the new restoration, the tooth will continue to function like any other tooth.
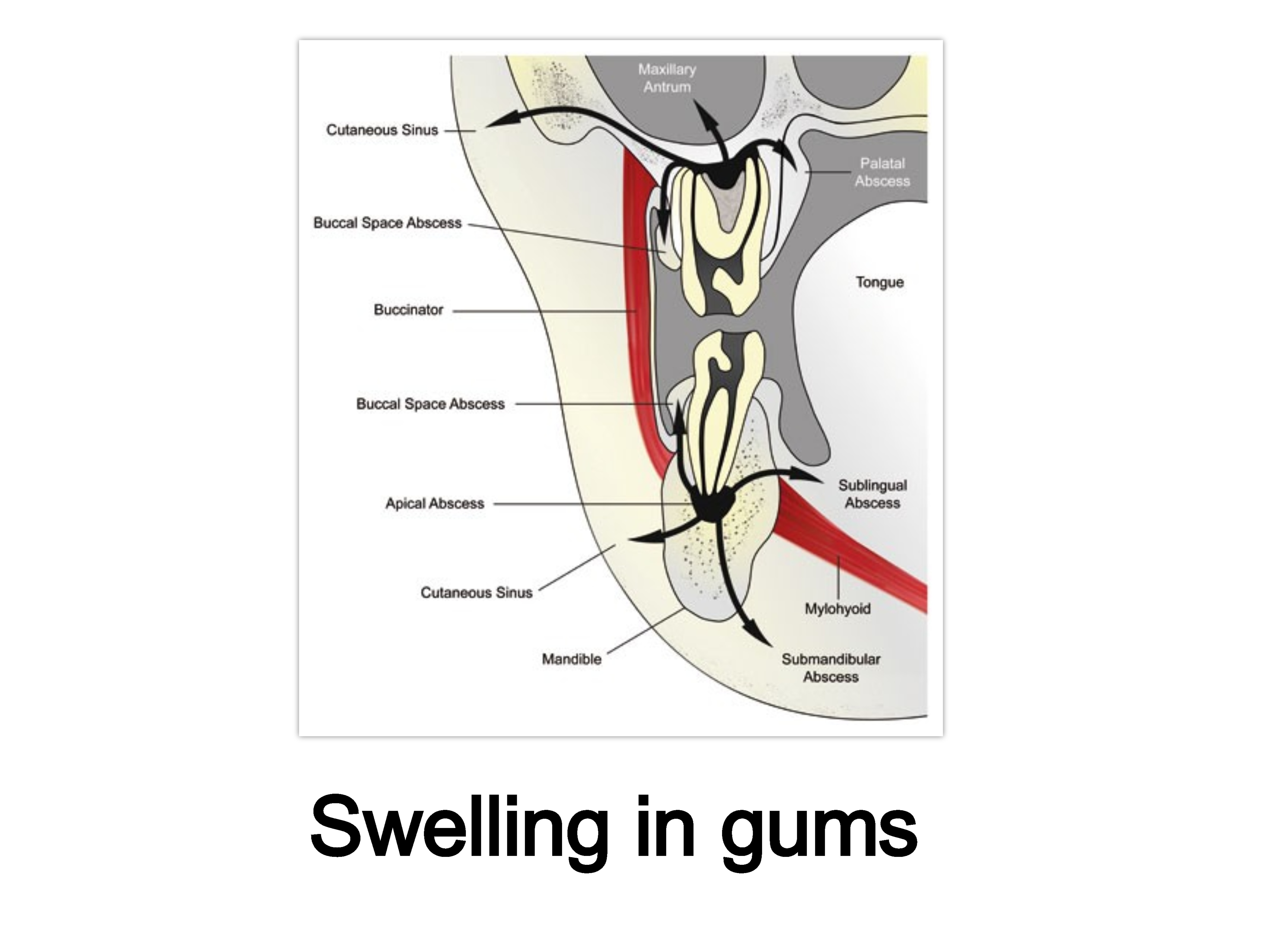
5. What is swelling in gums treatment ?
What - We can see mild to moderate bulge in gums near tooth which may or may not be painful and with or without sinus tract with pus.
Why - It is due to infected pulp or abscess below tooth, excessive food accumulation inside gums which eventually rottens and create pockets in gums, many times failed previous dental treatments.
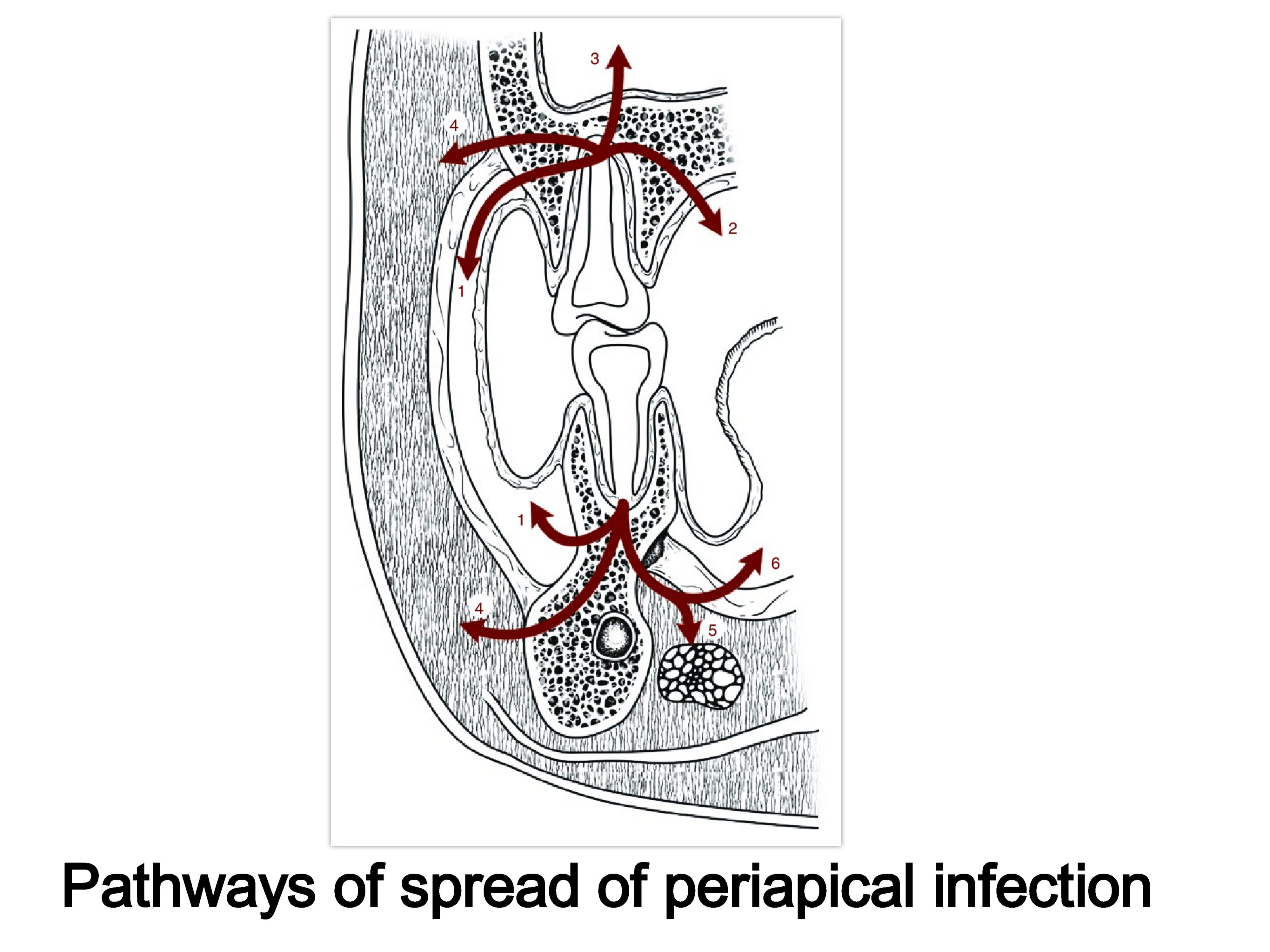
6. What is pathways of spread of periapical infection treatment ?
A periapical infection can spread along soft tissue and into various facial spaces, following the path of least resistance. The spaces that are most commonly affected include:
Subcutaneous: Can affect any tooth
Vestibular: Can affect any tooth
Buccal: Can affect any tooth, but especially maxillary teeth
Maxillary sinus: Can affect maxillary teeth
Submandibular: Can affect mandibular teeth
Sublingual: Can affect mandibular teeth
Masticator: Can affect mandibular teeth
Treatment options for a periapical infection include: Antibiotics, Incision and draining, Root canal therapy, and Tooth extraction.
To reduce the risk of periapical abscesses, you can: Practice good oral hygiene, Drink water with fluoride, Limit sugary foods and drinks, and Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and exams.